Strings In Java with Examples
What is a String in Java?
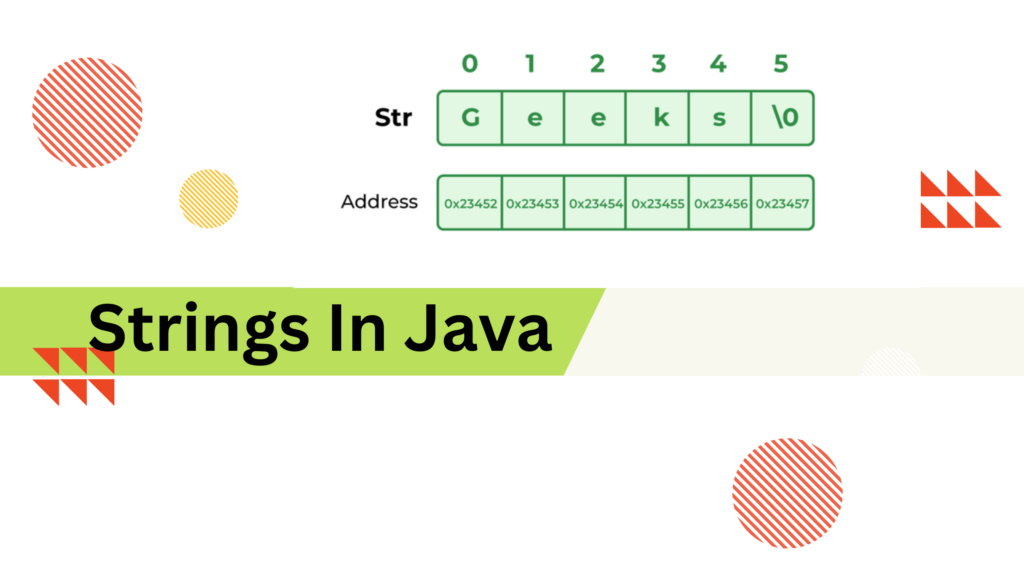
String can be defined as a sequence of characters i.e ‘Hello World” can be called String because it is made by sequence of characters.
In Java, a string is an object that represents a sequence of characters. It is a fundamental data type used to store and manipulate textual data. Strings in Java are instances of the java.lang.String class, which is a part of the Java Standard Library.
If you’re new to Java, our Do My Java Homework Help and Java Homework Help give full support to boost your grades and knowledge.
1 - How to Declare String in java?
In java String can be declare by two ways
- By new Keyword
- By String literal
- By new Keywork.
Java String is created by using a keyword “new”. With new keyword an Object of type String class is created inside memory.
public class STRING {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=new String(“Hello World”);
System.out.println(s);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
Explanation:
String s=new String (“Hello World”) in this line of code new keywork create object of class name String and Pass “Hello World” String to its constructor, a constructor create object in side heap memory and reference of that object is saved inside variable name s of type String.
In above picture new keyword create String class object in heap memory area having initialized value is “Hellow World” and its memory address is stored inside String variable name s which is created on Stack Memory Area.
- By String literal
public class STRING {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=“Hello World”;
System.out.println(s);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
Explanation:
String s= “Hello World” in this line of code a String “Hello World” is created on String pool area inside Heap Memory Area and its reference is saved inside variable name s of type String.
In above picture new keyword create String class object in heap memory area having initialized value is “Hellow World” and its memory address is stored inside String variable name s which is created on Stack Memory Area.
In java String can be declared in two ways
- By new Keyword
- By String literal
- By new Keyword.
Java String is created by using the keyword “new”. With a new keyword, an Object of type String class is created inside memory.
public class STRING {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=new String(“Hello World”);
System.out.println(s);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
Explanation:
String s=new String (“Hello World”) in this line of code new keywork create object of class name String and Pass “Hello World” String to its constructor, a constructor creates an object in side heap memory and the reference of that object is saved inside variable name s of type String.
In the above picture new keyword creates a String class object in the heap memory area having an initialized value is “Hellow World” and its memory address is stored inside String variable name s which is created on the Stack Memory Area.
- By String literal
public class STRING {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=“Hello World”;
System.out.println(s);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
Explanation:
String s= “Hello World” in this line of code a String “Hello World” is created on String pool area inside Heap Memory Area and its reference is saved inside variable name s of type String.
In the above picture new keyword creates a String class object in the heap memory area having an initialized value is “Hellow World” and its memory address is stored inside String variable name s which is created on the Stack Memory Area.
- By String literal
public class STRING {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=“Hello World”;
System.out.println(s);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
Explanation:
String s= “Hello World” in this line of code a String “Hello World” is created on String pool area inside Heap Memory Area and its reference is saved inside variable name s of type String.
In the above picture “Hello World” String is created inside the String Pool Area of Heap Memory Area and its Reference is Stored inside variable name s of Type String which is created on Stack Memory Area.
2 - What is the difference between String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder?
String is immutable while StringBuffer and StringBuilder are mutable, when we say immutable then it means we cannot modify the Content of the Variables at run time.
- Why String is immutable?
public class STRING {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s=“Hello World”;
s=”how are you”;
System.out.println(s);
}
run:
how are you
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
When this line String s=”Hello World”; execute a “Hello World” String created in String pool area inside Heap Memory Area and reference is saved inside variable name s whose type is string, after this when s=”how are you”; line execute by compiler than a new string “how are you” is created on String pool area and its reference is saved inside s variable, now s variable is pointing out on newly created string “how are you” and old string “Hello World” is dereferenced and will clean out by garbage collector routine.
- Why StringBuffer/StringBuilder are Mutable?
In mutable every time when you modify the string there is no need to crate new string on Heap memory area, it’s just modified old content with new once.
StringBuffer and StringBuilder are mutable objects in Java. They provide append(), insert(), delete(), and substring() methods for String manipulation.
public class StringBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“Hello “);
sb.append(“World”);
System.out.println(sb);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
When StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(“Hello “); line is executed a String “Hello “ is created on Heap Memory Area and reference is stored inside variable sb of type StringBuffer, now after that when sb.append(“World”) line executed than String “World” is concatenated with String Hello on Heap Memory Area.
3 - How to concatenate String in java?
- When we create String with new keywork using classes StringBuffer or StringBuilder than we use append method of these class to concatenate the two strings.
public class StringConcatinate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer (“Hello “);
sb.append(“World”);
System.out.println(sb);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
- When we create a string using string literal then there are 2 methods to concatenate the string
- Using + operator
- Using concat() method
- Using + operator
public class StringConcatinate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= “Hello“;
String s2=”World”;
String s3=s1+s2;
System.out.println(s3);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
- Using concat() method
public class StringConcatinate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= “Hello“;
String s2= “World“;
String s3= s1.concat(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
when we concatenate String using + operator or concate() function a new string “Hellow World” is created inside String pool Area and its reference is saved inside variable name s3 of type String created on Stack Memory Area.
- Why equals () method of the String class is used in Java?
equals () method belongs to the String class, which is used to compare the content of two string variables.
public class EQUAL {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= “Hello“;
String s2= “Hello“;
If(s1.equals(s2))
{
System.out.println(“s1 contents are equal to s2”);
}
}
run:
s1 contents are equal to s2
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code, s1 variable and s2 variable both contain String Hello, and the equals() method compares the contents of both variables in the side if condition which is true because both contain String Hello, so if the condition becomes true and “s1 contents are equal to s2” message printout on the console.
4 - What is the Difference between ‘==’ operator and ‘equal ()’ method in Java?
equal() method is used to compare contents of the two variables while == operator is used to compare memory addresses of the two variables
String s1 = “Hello”;
String s2 = “Hello”;
when String s1 = “Hello”; line execute then a String Hello is created inside String pool area on Heap and memory address of String “Hello” is stored inside variable s1 which is 0x12343, now when String s2 = “Hello”; is executed then what jvm (java virtual machine) does here it can not create another “Hello” String on String pool Area, rather then it first check whether String “Hello” is already created on String pool area or not if yes then it store memory address of that “Hello” String which is 0x12343 inside s2 variable, now both s1 and s2 are pointing to same memory address inside String pool memory Area.
If (s1 == s2) this if condition compare the memory addresses saved inside s1 and s2 variables which is 0x12343 .
If( s1.equals(s2)) while this if condition compare contents saved at 0x12343 memory address which is Hello.
So == operator is used to compare the memory address while equals() method is used to actually compare the contents which is saved at that memory address.
- How we find the Length of the String in Java?
length() method of String class is used to count the number of characters inside String.
public class StringLength {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s= “Hello World“;
int charLength= s.length();
System.out.println(charLength);
}
run:
11
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet s.length() return the length of String “Hello World” which is 11 including white space also.
- How to compare case-insensitive string in java?
For case-insensitive string comparisons java use String class method equalsIgnoreCase() which return true if both String are equal and if not than return false.
public class StringComparison {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= “HELLO WORLD“;
String s2= “hello world“;
boolean res=s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2);
System.out.println(res);
}
run:
true
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet s1 variable contain upper letter string while s2 contain string with lower case letters, code line s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2) compare both variables contents, ignoring upper or lower case and if both strings are equal than it return true and if string are not equal than return false.
- How to extract a substring from a string in java?
To get sub string from string java use subString() function of String class.
subString() function take 2 arguments startIndex and endIndex.
startIndex : starting index is inclusive
endIndex : ending index is exclusive
public class SubString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1= “HELLO WORLD“;
String s2= s1.subString(0,5);
System.out.println(s2);
}
run:
HELLO
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet s1 variable contain String “HELLO WORLD”.
s1.subString(0,5) return sub string starting form 0 index and ending at 4 index which is HELLO while index 5 is exclusive.
Index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
letters | H | E | L | L | O |
5 - How we divide the string into array of substrings in Java?
The split() method divides the string at the specified regex and returns an array of substrings.
public class SplitMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String textStr = “hellow world, creating java tutorials, become a programmer is my dream“;
String[] result = textStr.split(“,”);
for (String str : result) {
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
run:
hellow world
creating java tutorials
become a programmer is my dream
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet textStr variable contain string which is separated by commas. textString.split(“,”) line spilt the string at the position where comma occurred and convert the string into array.
6 – How do I convert a string to uppercase or lowercase?
To convert lower case to upper case java use toUpperCase() function of the String class and to convert upper case to lower case java use toLowerCase() function of the string class.
public class UpperLowerCase {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = “Hello World“;
System.out.println(txt.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(txt.toLowerCase());
}
}
run:
HELLO WORLD
hello world
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet txt string contain “Hello World” String, toUpperCase() function convert “Hello World” to all Upper case letters while function toLowerCase() convert it to all lower case letters.
7 – How can I remove whitespace from the beginning and end of a string in Java?
trim() function of String class is used for removing of whitespace from the beginning and end of a string in java.
public class Trim {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = “ Hello World “;
txt=txt.trim();
System.out.println(txt);
}
}
run:
Hello World
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet trim() function remove whitespace from start and end of the String “Hello World”
8 – How we can get specific character from the String in Java?
charAt() is the String class function which return the character at specific index. charAt() function take index as an argument and return character which is at that index.
public class CharAt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = “Hello World”;
char res=txt.charAt(7);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
run:
o
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet charAt(7) function take index 7 as an argument and return the character at index 7 which is o.
|
Index |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
character |
H |
e |
l |
l |
o |
W |
o |
r |
l |
d |
At index 5 there is whitespace.
9 – How can I replace characters in a string?
To replace characters in string java use replace() function of String class, replace(old_string, new_string) function take 2 arguments 1st one old_sting and 2nd is new_string.
replace function replace old_string with new_string.
public class ReplaceString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = “Hello World“;
txt = txt.replace(“World”, “Man”);
System.out.println(txt);
}
}
run:
Hello Man
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet replace(“World”,”Man”) function taking argument “World” which is old_string and “Man” which is new_string, function replace old_string with new_string
10 – How to Converting String into numeric Data Type in java?
Java String class provide two ways to convert String into numeric data types.
- Integer.parsInt() function
- Integer.valueOf() function
- Integer.parsInt()
This method returns the string as a primitive type int.
public class ParseInt{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = “30“;
int parsValue = Integer.parseInt(txt);
System.out.println(parsValue);
}
}
run:
30
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In above code snippet txt variable contain 30 as string, while Integer.parseInt(txt) convert this string into int value and saved inside parsValue variable.
- Integer.valueOf()
This method returns the string as an integer object.
public class ValueOf{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String txt = “30“;
Integer parsValue = Integer.valueOf(txt);
System.out.println(parsValue);
}
}
run:
30
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
In the above code snippet Integer.valueOf(txt) return Integer object of value 30, which is saved inside variable parsValue.
Other function used for converting string to numeric values.
|
Function |
Description |
|
Double.parseDouble() |
Convert string to decimal primitive value |
|
Double.valueOf() |
Convert string to decimal class object |
|
Float.parseFloat() |
Convert string to float primitive value |
|
Float.valueOf() |
Convert string to float class object |
Q & A (Questions And Answers)
How you define the String in Java?
String can be defined as a sequence of characters, that’s makes a word or sentence.
Example “Hello World” can be called String because it is made by sequence of characters.
How many ways to declare a String in Java?
There are 2 ways to declare a String in java
- By new Keyword
- By String literal
By using “new” keyword on which memory area the String were created?
By using “new” keyword the String were created on Heap Memory area.
Why String is immutable in java?
String is immutable in java because we cannot modify or change the value of string once its created-on memory. If we change or modify the value of string then a new copy of whole the string is created on memory area and old one is removed by garbage collector routine.
Why StringBuffer/StringBuilder is mutable in java?
StringBuffer and StringBuilder are mutable in java because when we create string using StringBuilder or StringBuffer then its created-on memory area once, after that we can change or modify the original string without creating again on memory area.
Which method is used to concatenate the String when String is created by using StringBuilder or StringBuffer class?
append() method is used to concatenate the String when String is created by using StringBuilder or StringBuffer class
When we use + operator to concatenate the String in Java?
We use + operator to concatenate the String in java when we create string using string literal.
For which purpose “==” operator is used in Java?
==” operator is used to compare memory addresses of the two variables.
For which purpose equal() method is used in Java?
equal() method is used for comparing the content of two variables.
Which method is used to find the length of String in Java?
length() method of String class is used to find the length of String in Java.
How to compare case-insensitive String in Java?
equalsIgnoreCase() method is used to compare case-insensitive string in java , it’s return true when both string are equal.
How to extract sub string from string in java?
subString() method of String class is used to extract sub string from string in java it’s takes startIndex and endIndex as arguments
Which method is used to divide the string into array of substrings in Java?
split() Method of String class is used to divide the string into array of substrings in Java.
toUpperCase() function of String class is used for which purpose in Java?
toUpperCase() function is used to convert the string into all upper case letters.
What Is the purpose of using toLowerCase() method in Java?
toLowerCase() function is used to convert the string into all lower case letters.
What is the use of trim() function in Java?
trim() function of String class is used for removing of whitespace from the beginning and end of a string in java.
How to get specific character from String in Java?
charAt() is the String class function which return the character at specific index. charAt() function take index as an argument and return character which is at that index.
Which function is used for replacing the character inside String in Java.
replace() function is used for replacing the character inside String in java. replace() function take 2 arguments 1st one old_sting and 2nd is new_string.
There are how many ways String class provide to convert String into numeric Data in Java?
- Java String class provides two ways to convert String into numeric data types.
- Integer.parsInt() function
- Integer.valueOf() function
Strings In Java with Examples Read More »